The Redshift task events architecture diagram is an essential resource for comprehending the dependencies, event management, and execution flow of Amazon Redshift’s robust data processing environment. Redshift is a cloud-based data warehousing system that is an essential component of Amazon Web Services (AWS) and helps businesses effectively handle and analyze massive amounts of data. Data processing jobs operate easily thanks to a well-designed task events architecture that precisely orchestrates tasks and integrates several components.
Understanding Amazon Redshift Task Events Architecture Diagram
Understanding Amazon redshift task events architecture diagram is crucial before delving into the task events architecture because the system’s components are interconnected with the task events. There are several main components that make up the Redshift architecture:
- Leader Node: This is the system’s brain. It is in charge of creating query plans, maintaining client relationships, and coordinating queries. Although it doesn’t undertake a lot of calculations, the leader node is essential to coordinating activities throughout the cluster.
- Compute Nodes: These are the system’s workhorses. They manage the data processing and run the queries. Each node slice, which is a smaller unit of computation, carries out parallel processing. Through the distribution of jobs among several computational resources, this approach optimizes Redshift’s performance.
- Redshift Managed Storage (RMS): Large datasets can be handled and retrieved quickly because to Redshift’s controlled storage. It adapts easily to changes in processing demands and data volume.
- Backup and Recovery: Your data is always recoverable thanks to Redshift’s automated backups. Historical snapshots are preserved, and backups are automatically carried out on a regular basis.
The task events architecture is what guarantees that data processing is carried out effectively, with each action triggered and handled in the correct sequence, even though all of these components interact during the task execution flow.
What is Task Events in Redshift?
In Amazon Redshift, task events refer to the actions that occur when a job or a set of processes in a data pipeline are executed. A task event could be a database operation, a data transformation, or even a data load job. Task events are crucial for managing data flows, automating pipelines, and ensuring that complex tasks occur in a sequence without human intervention.
Task events typically include:
- Data Load Events: The execution of data loading processes from Amazon S3 or other external sources.
- Data Transformation Events: Transforming raw data into a usable format by running SQL queries or custom scripts.
- Error Handling Events: Capturing failures or performance issues during the execution of data jobs.
- Completion Events: Indicating the successful completion of a task or job.
The Redshift task events architecture diagram visually represents these events, how they are triggered or sequenced, as well as the tasks they are linked to. Usually, systems that automate complicated workflows, such Apache Airflow or AWS Step Functions, are used to organize these events.
The Role of Orchestration Tools in Task Events
Redshift task event orchestration is crucial for handling intricate operations. Redshift is frequently connected with orchestration tools, such as Apache Airflow and AWS Step Functions, to automate and track task execution. These technologies handle dependencies between different stages of the data pipeline, make ensuring that actions are carried out in the right order, and set off events based on certain situations.
AWS Step Functions, for instance, can manage the steps involved in a standard ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline, which includes extracting data from an S3 bucket, transforming it in Redshift, and then loading the modified data back into an S3 bucket or another data storage. The orchestration tool will oversee the execution of each of these stages, which may be thought of as task events.
Task Events and Redshift’s Scalability
Redshift task event orchestration is crucial for handling intricate operations. Redshift is frequently connected with orchestration tools, such as Apache Airflow and AWS Step Functions, to automate and track task execution. These technologies handle dependencies between different stages of the data pipeline, make ensuring that actions are carried out in the right order, and set off events based on certain situations.
AWS Step Functions, for instance, can manage the steps involved in a standard ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline, which includes extracting data from an S3 bucket, transforming it in Redshift, and then loading the modified data back into an S3 bucket or another data storage. The orchestration tool will oversee the execution of each of these stages, which may be thought of as task events.
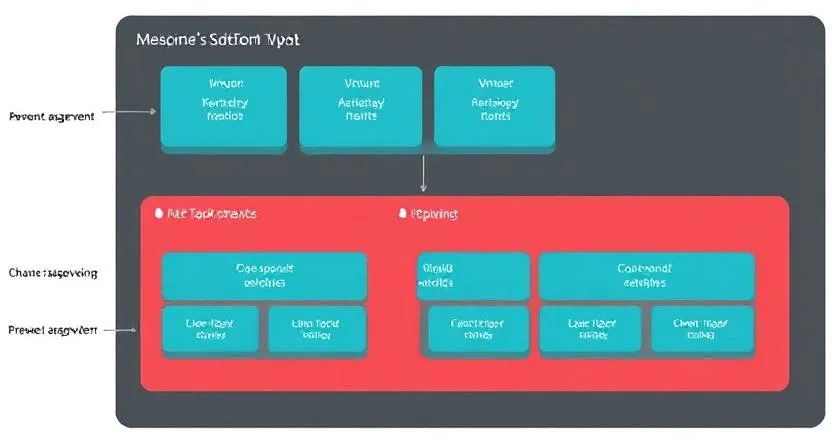
The Redshift task events architecture diagram typically shows how each event interacts with various parts of Redshift, including compute nodes, storage, and orchestration systems. It also highlights how tasks are parallelized, which helps achieve high throughput and low latency even in large-scale data environments.
Visualizing Task Events with Redshift Task Events Architecture Diagram
A Redshift task events architecture diagram typically includes several key components:
- Task Events Nodes: These represent the various tasks within the data pipeline, such as data loading, transformations, or complex computations.
- Orchestration Layer: This is typically a tool like AWS Step Functions or Apache Airflow, which schedules and manages the task events based on their dependencies.
- Event Dependencies: These are the relationships between different tasks. For example, a data load event might need to be completed before a transformation event can be triggered.
- Failure Handling: The diagram shows how the architecture handles failures in task execution. For instance, a task event failure might trigger an alert or a retry mechanism.
- Data Flow: The diagram illustrates the flow of data between the tasks and the storage systems, such as the Redshift data warehouse and external storage like Amazon S3.
Teams can more effectively see the orchestration of data pipelines by employing a task events architecture diagram. This ensures that data processing jobs are carried out efficiently and that all tasks run in the best possible order with the fewest possible delays.
Best Practices for Implementing Task Events in Redshift Task Events Architecture Diagram
Take into account the following best practices to maximize task event execution and orchestration in Redshift:
- Ensure Task Parallelization: Leverage Redshift’s MPP architecture to parallelize data processing tasks, reducing the overall time needed to complete large data jobs.
- Monitor Task Events: Implement robust monitoring mechanisms to track the progress of tasks and events in real-time. AWS CloudWatch is an excellent tool for this purpose.
- Implement Error Handling: Design error handling into the task events architecture to ensure that failures are automatically detected, and corrective actions (such as retries) are triggered without manual intervention.
- Automate Data Pipelines: Use orchestration tools like Apache Airflow or AWS Step Functions to automate data workflows and ensure that task events are triggered and executed in the correct order.
- Use Efficient Storage Solutions: Integrate Amazon S3 with Redshift to efficiently load and store large datasets, and ensure that the storage infrastructure supports the demands of the task events architecture.
Conclusion
The Redshift task events architecture diagram is an essential tool for understanding how data workflows are managed within Amazon Redshift.Teams can create data pipelines that are more effective and scalable by visualizing the connections between tasks, events, and orchestration tools. Redshift can be integrated with orchestration technologies such as Apache Airflow or AWS Step Functions to automate job events, increasing the reliability of data processing and decreasing the need for user intervention. When these technologies are in place, Redshift transforms into a strong and effective instrument for managing massive data operations, guaranteeing quick, dependable, and secure data processing for contemporary businesses.












Leave a comment